
Your mouth is the gateway to your body's health, yet millions of people ignore critical warning signs that could prevent serious health complications. Recent studies show that poor oral health is linked to heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and even Alzheimer's disease. This comprehensive guide reveals the 10 warning signs you shouldn't ignore and provides actionable solutions to transform your oral health.
⚠️ Critical Health Alert
Did you know that gum disease affects over 47% of adults over 30 in the United States? Even more alarming, advanced gum disease increases your risk of heart attack by 28% and stroke by 13%. The good news? Most oral health problems are completely preventable with the right knowledge and approach.
The Hidden Connection: How Your Mouth Affects Your Entire Body
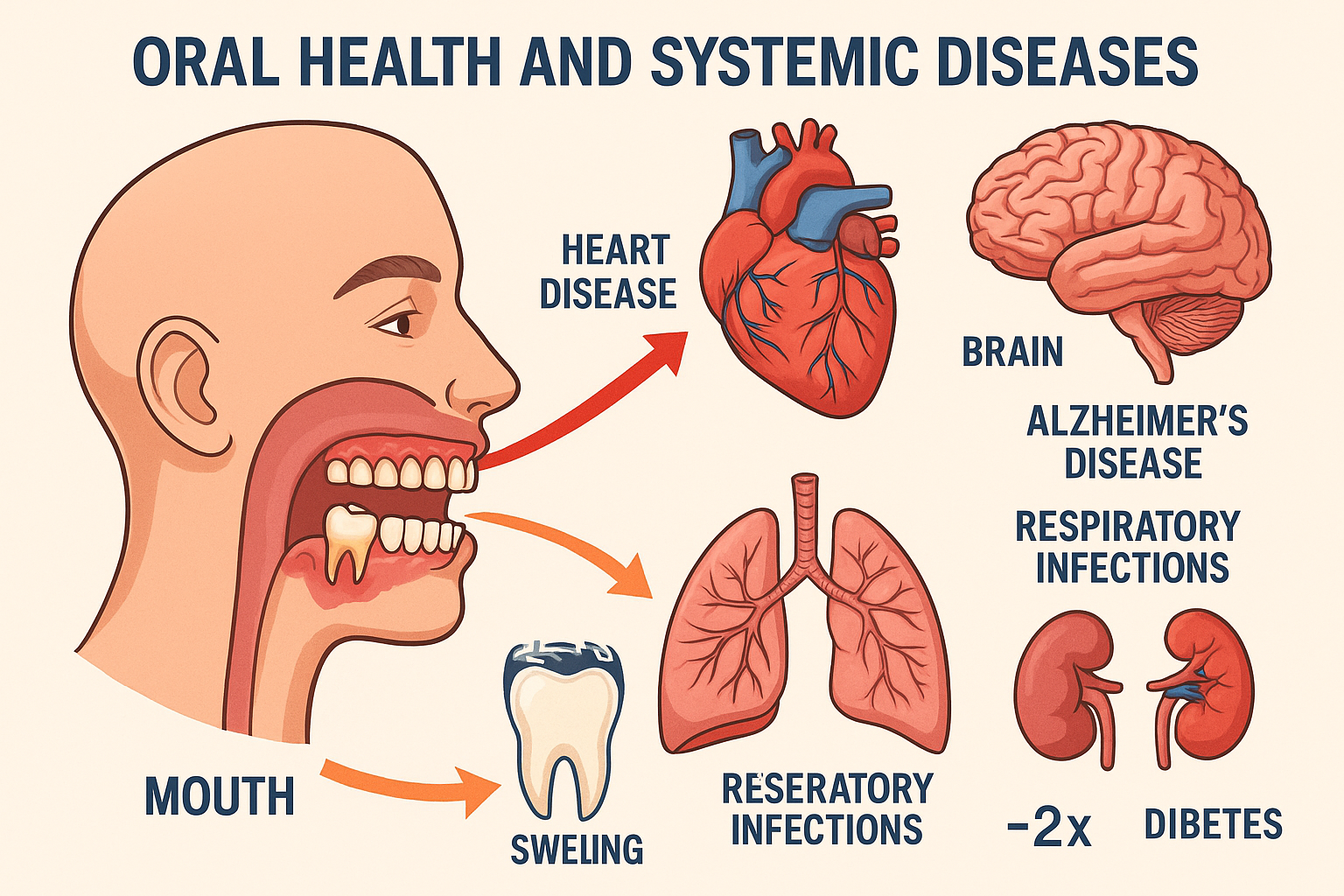
The human mouth contains over 700 species of bacteria, creating a complex ecosystem that directly impacts your overall health. When this delicate balance is disrupted, harmful bacteria can enter your bloodstream through inflamed gums, triggering inflammatory responses throughout your body.
Dr. Thomas Van Dyke, a leading researcher at the Forsyth Institute, explains that "the mouth is not separate from the body." His groundbreaking research has shown that oral bacteria can travel through the bloodstream and contribute to the formation of arterial plaques, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The oral-systemic connection extends far beyond heart disease. Recent studies have identified links between poor oral health and:
🔬 Scientific Breakthrough
A 2024 study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that people with severe gum disease had a 70% higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease. The study followed 8,275 participants over 26 years, providing compelling evidence of the mouth-brain connection.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Control
The relationship between diabetes and gum disease is bidirectional. High blood sugar levels create an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive in your mouth, while gum disease makes it harder to control blood sugar levels. This creates a dangerous cycle that can lead to serious complications.
People with diabetes are three times more likely to develop severe gum disease, and those with gum disease have a 50% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The inflammation caused by gum disease can make cells more resistant to insulin, the hormone that controls blood sugar.
Respiratory Infections and Pneumonia
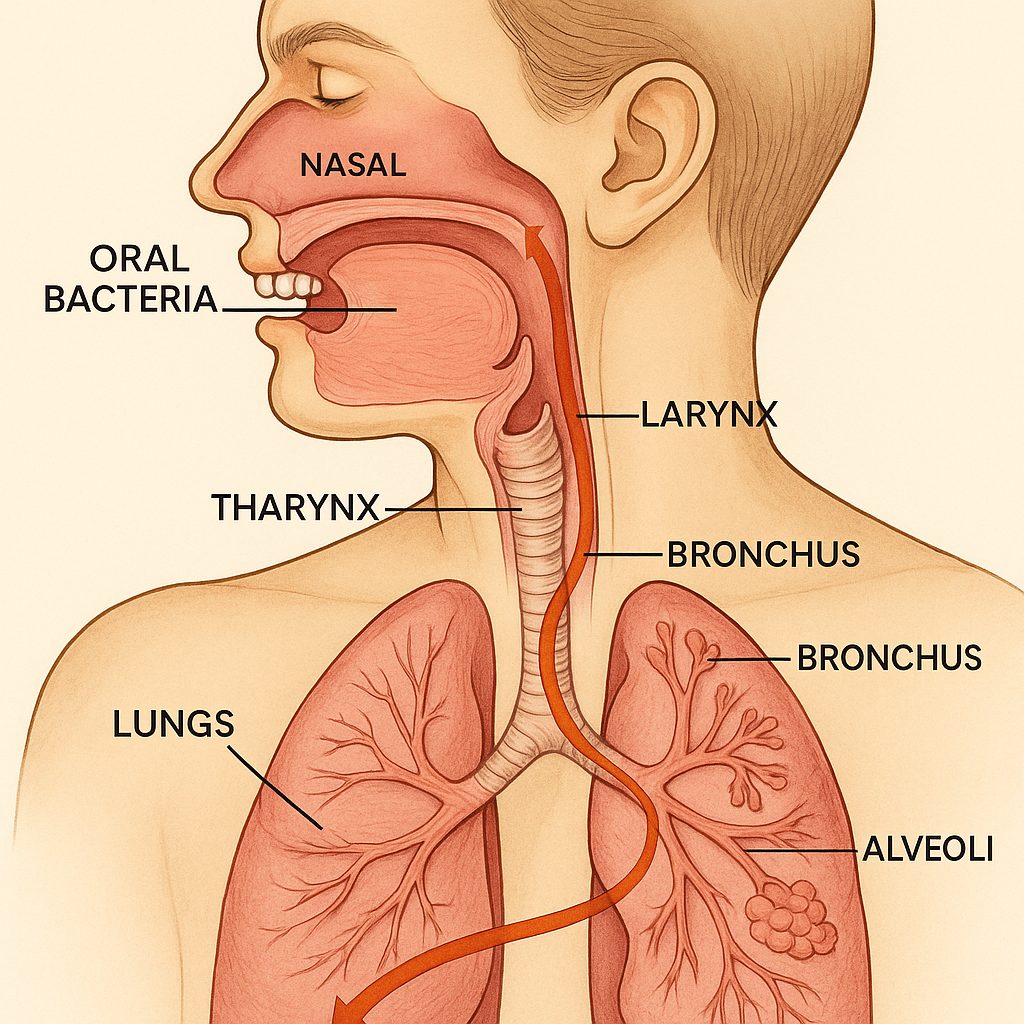
Bacteria from your mouth can be inhaled into your lungs, particularly during sleep. This is especially dangerous for elderly individuals or those with compromised immune systems. Studies show that improving oral hygiene in nursing home residents reduced the incidence of pneumonia by 40%.
Pregnancy Complications
Pregnant women with gum disease face increased risks of premature birth, low birth weight babies, and preeclampsia. The hormonal changes during pregnancy can exacerbate existing gum problems, making professional dental care and proper oral hygiene even more critical.
Research published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that treating gum disease during pregnancy reduced the risk of preterm birth by 84%. This highlights the importance of maintaining excellent oral health throughout pregnancy.
The 10 Warning Signs You're Ignoring (And Why They're Dangerous)
Most people dismiss early warning signs of oral health problems as minor inconveniences. However, these seemingly small issues can escalate into serious health threats if left untreated. Here are the 10 critical warning signs you should never ignore:
1. Bleeding Gums During Brushing or Flossing
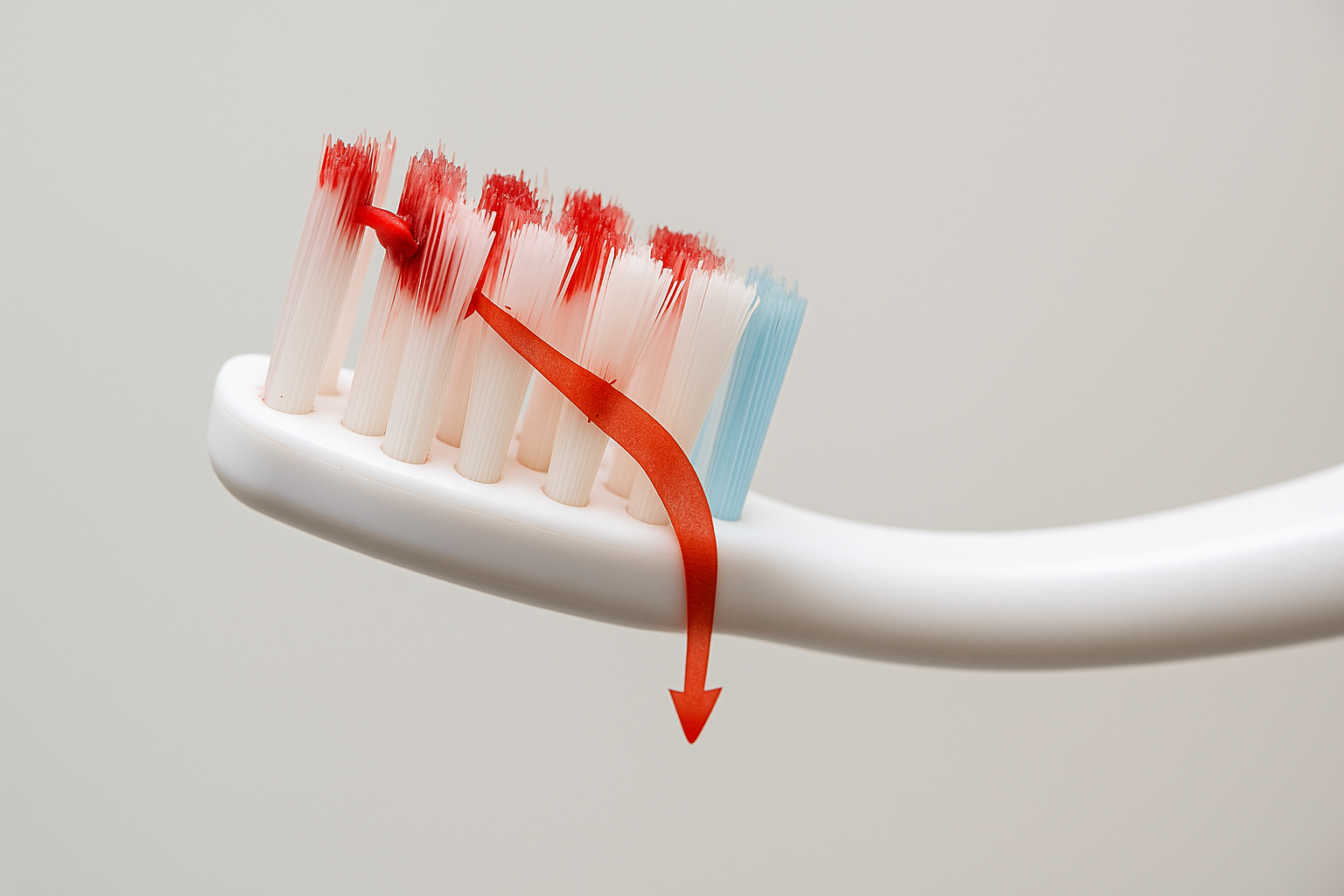

Many people believe that bleeding gums are normal, especially when starting a new oral hygiene routine. This is a dangerous misconception. Healthy gums should never bleed during normal brushing or flossing.
Bleeding gums are typically the first sign of gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. At this stage, the condition is still reversible with proper care. However, if ignored, gingivitis progresses to periodontitis, a more serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and systemic health problems.
🚨 The Hidden Danger
When your gums bleed, you're creating an open pathway for bacteria to enter your bloodstream. This bacteremia can lead to infective endocarditis, a potentially life-threatening infection of the heart's inner lining. People with certain heart conditions are at particularly high risk.
The good news is that bleeding gums often respond quickly to improved oral hygiene and targeted nutritional support. Studies show that supplements containing specific probiotics and anti-inflammatory compounds can reduce gum bleeding by up to 60% within just two weeks.
2. Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
While occasional bad breath is normal, persistent halitosis that doesn't improve with brushing, flossing, or mouthwash use indicates a deeper problem. Chronic bad breath affects approximately 25% of the population and can have serious underlying causes.

Persistent bad breath is often caused by:
• Bacterial overgrowth in the mouth, particularly anaerobic bacteria that produce sulfur compounds
• Gum disease and periodontal pockets that harbor harmful bacteria
• Dry mouth (xerostomia), which reduces the natural cleansing action of saliva
• Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, or kidney problems
Research published in the International Journal of Dental Hygiene found that 90% of bad breath cases originate in the mouth, but the remaining 10% can indicate serious systemic health issues. For example, a sweet, fruity breath odor can signal diabetic ketoacidosis, a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes.
💡 Professional Tip
The "spoon test" can help you assess your breath objectively. Scrape the back of your tongue with a spoon and smell it after it dries. This gives you a more accurate assessment of your breath than breathing into your cupped hands.
3. Receding Gums
Gum recession is often gradual and painless, making it easy to ignore until significant damage has occurred. However, receding gums expose the tooth roots, leading to sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and eventual tooth loss.
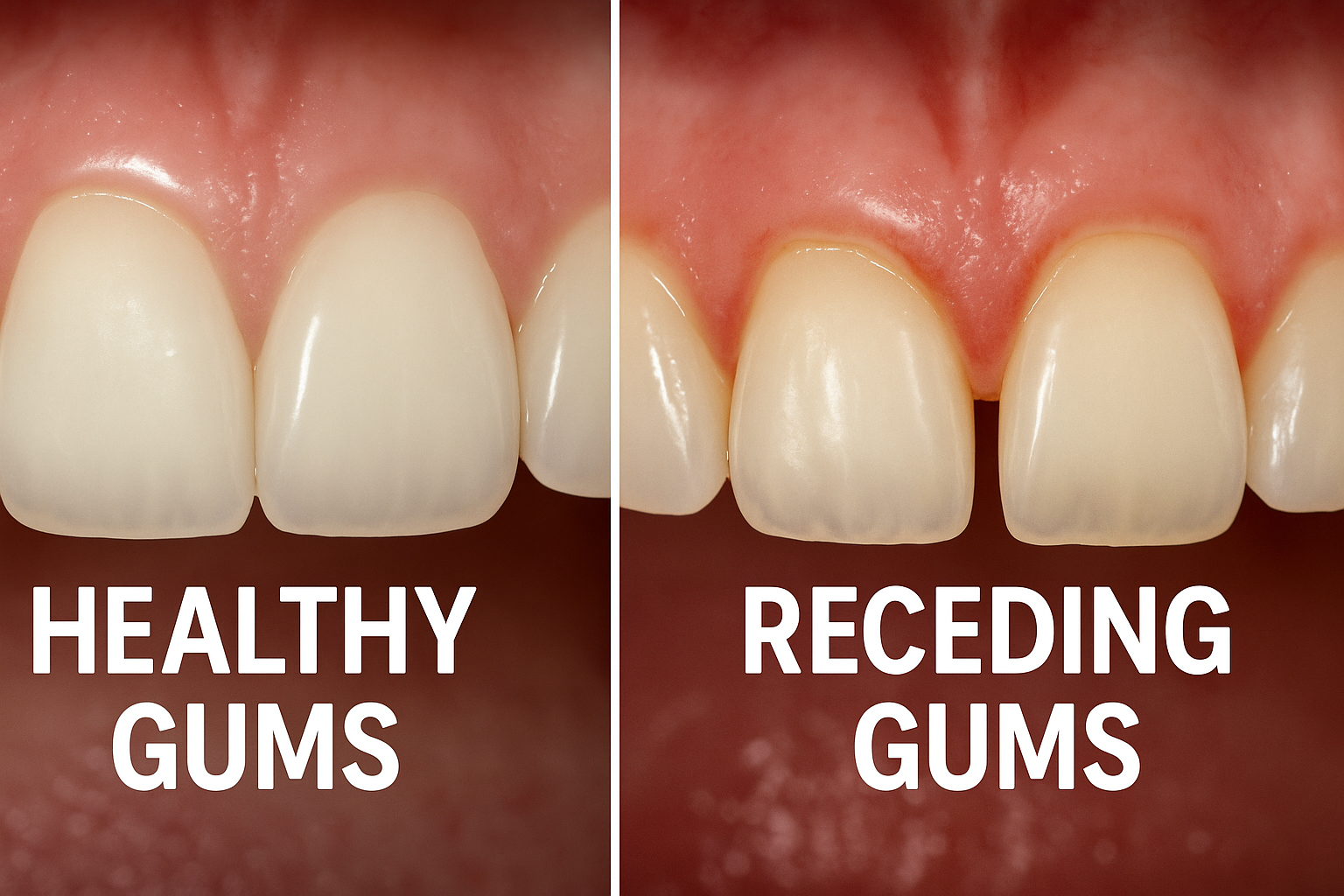
Common causes of gum recession include:
• Aggressive brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush
• Gum disease and chronic inflammation
• Genetic predisposition (family history of gum problems)
• Hormonal changes, particularly in women
• Tobacco use in any form
• Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism)
Once gum tissue recedes, it doesn't naturally regenerate. This makes early detection and intervention crucial. Advanced treatments like guided tissue regeneration or gum grafting may be necessary to restore lost tissue and protect the teeth.
4. Loose or Shifting Teeth
Adult teeth should remain firmly anchored in their sockets throughout life. Any looseness or shifting is a serious warning sign that requires immediate professional attention.
Tooth mobility can indicate:
• Advanced periodontal disease with bone loss
• Trauma or injury to the tooth or surrounding structures
• Bite problems or excessive force on certain teeth
• Bone loss due to osteoporosis or other systemic conditions
⚠️ Emergency Situation
If you notice sudden tooth mobility following an injury, seek emergency dental care immediately. Quick intervention can often save the tooth and prevent complications.
5. Chronic Jaw Pain or TMJ Symptoms
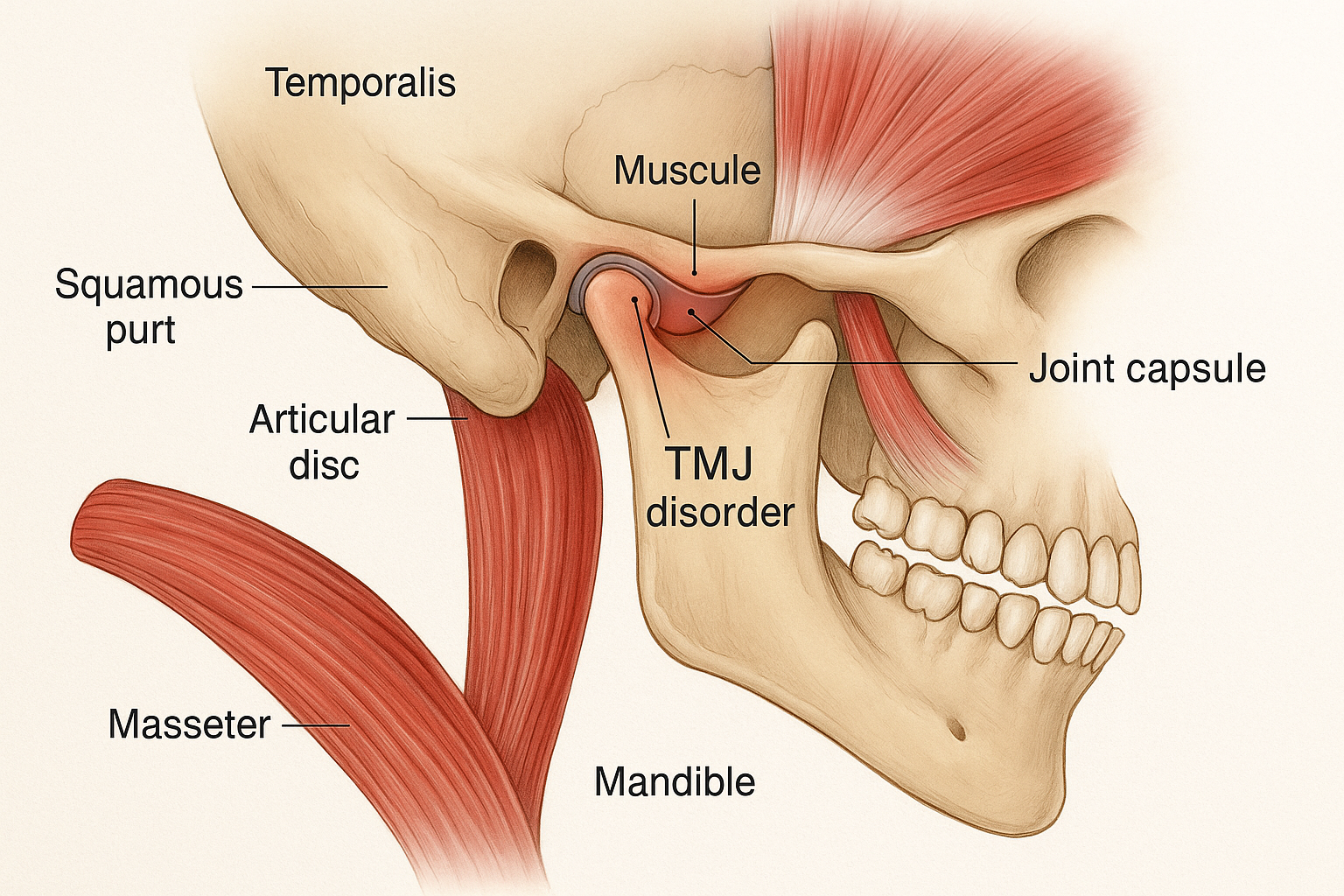
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders affect over 10 million Americans and can significantly impact quality of life. Symptoms include jaw pain, clicking or popping sounds, difficulty opening the mouth, and headaches.
While TMJ disorders are often considered dental problems, they can have far-reaching effects on your overall health. Chronic jaw pain can lead to:
• Sleep disruption and sleep apnea
• Chronic headaches and migraines
• Neck and shoulder pain
• Difficulty eating and nutritional deficiencies
• Increased stress and anxiety
Recent research has also linked TMJ disorders to increased inflammation throughout the body, potentially contributing to cardiovascular disease and other systemic conditions.
6. White or Red Patches in the Mouth
Any unusual patches, spots, or lesions in your mouth should be evaluated by a dental professional immediately. These can be early signs of oral cancer, which affects over 54,000 Americans annually.
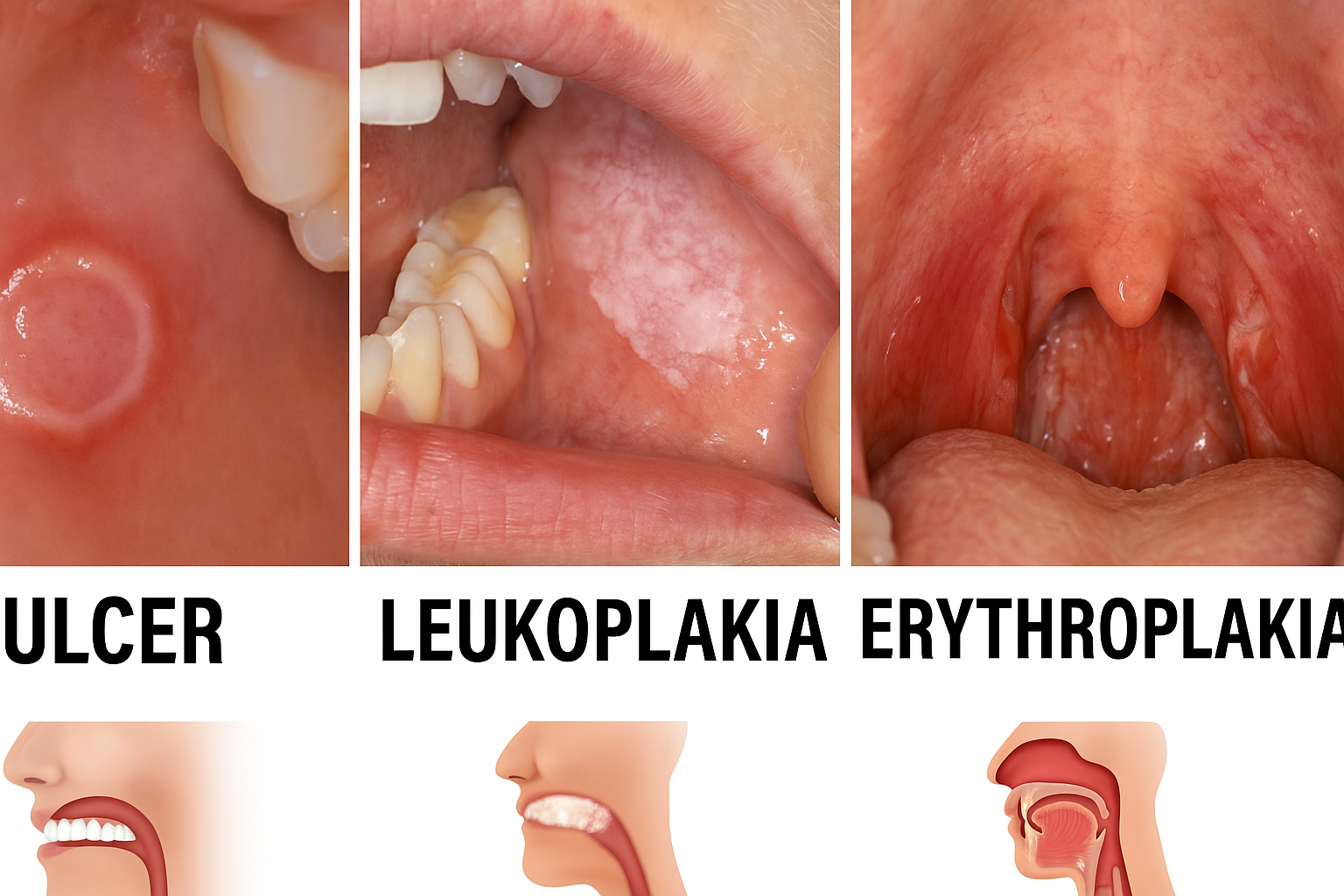
Common types of oral lesions include:
• Leukoplakia: White patches that cannot be wiped away
• Erythroplakia: Red patches or spots
• Mixed lesions: Patches with both red and white areas
• Ulcers that don't heal within two weeks
While not all oral lesions are cancerous, early detection is crucial for successful treatment. The five-year survival rate for oral cancer is 84% when caught early, but drops to 39% when diagnosed at advanced stages.
7. Chronic Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by neutralizing acids, washing away food particles, and controlling bacterial growth. Chronic dry mouth significantly increases the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and oral infections.
Common causes of dry mouth include:
• Medications (over 400 medications list dry mouth as a side effect)
• Medical conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cancer treatments
• Dehydration and inadequate fluid intake
• Mouth breathing, often due to sleep apnea or nasal congestion
💧 Saliva Facts
A healthy person produces 1-2 liters of saliva daily. Saliva contains over 3,000 proteins, including antibodies, enzymes, and growth factors that protect and repair oral tissues. When saliva production decreases, the mouth becomes vulnerable to bacterial overgrowth and tissue damage.
8. Frequent Canker Sores or Oral Ulcers
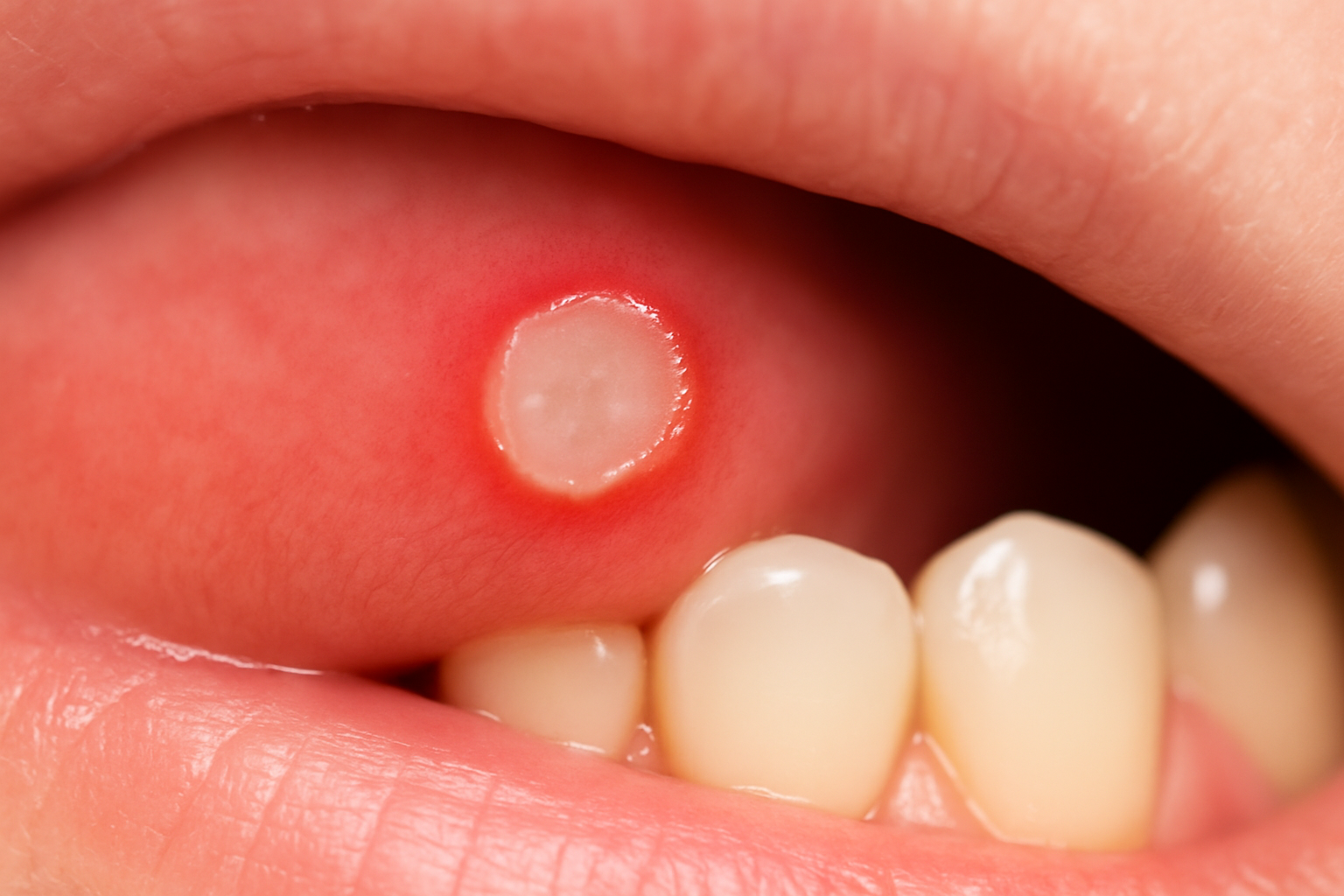
While occasional canker sores are common and usually harmless, frequent outbreaks can indicate underlying health issues or nutritional deficiencies. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis affects up to 25% of the population and can significantly impact quality of life.
Frequent canker sores may be associated with:
• Nutritional deficiencies (B12, folate, iron, zinc)
• Autoimmune conditions
• Hormonal fluctuations
• Food sensitivities or allergies
• Stress and compromised immune function
9. Tooth Sensitivity to Hot, Cold, or Sweet Foods
Tooth sensitivity affects over 40 million adults in the United States and is often dismissed as a minor inconvenience. However, sensitivity can indicate serious underlying problems that require professional treatment.
Tooth sensitivity occurs when the tooth's protective enamel layer is worn away or when gums recede, exposing the underlying dentin. This can be caused by:
• Aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush
• Acidic foods and drinks that erode enamel
• Teeth grinding or clenching
• Gum disease and recession
• Cracked or damaged teeth
🦷 Enamel Protection Tip
Wait at least 30-60 minutes after consuming acidic foods or drinks before brushing your teeth. Brushing immediately after acid exposure can actually accelerate enamel erosion when the enamel is temporarily softened.
10. Changes in Taste or Persistent Metallic Taste
Alterations in taste perception can indicate various oral and systemic health problems. A persistent metallic taste, in particular, can be a sign of gum disease, medication side effects, or underlying medical conditions.
Taste changes can be caused by:
• Gum disease and oral infections
• Dry mouth and reduced saliva production
• Medications and medical treatments
• Nutritional deficiencies, particularly zinc and vitamin B12
• Neurological conditions affecting taste perception
The Revolutionary Role of Oral Health Supplements
While traditional oral hygiene practices remain essential, cutting-edge research has revealed the powerful role that targeted nutritional supplements can play in supporting oral health. Unlike conventional approaches that focus solely on removing bacteria, modern oral health supplements work to restore balance to the oral microbiome and support the body's natural healing processes.
The Science Behind Oral Health Supplements
Recent breakthroughs in microbiome research have revolutionized our understanding of oral health. Scientists now know that the mouth contains a complex ecosystem of beneficial and harmful bacteria, and maintaining the right balance is crucial for preventing disease.
Dr. Wenyuan Shi, a leading researcher at UCLA's School of Dentistry, explains that "the future of oral health lies not in killing all bacteria, but in promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria that naturally suppress harmful pathogens."
This paradigm shift has led to the development of targeted supplements that:
• Introduce beneficial probiotic strains specifically selected for oral health
• Provide essential nutrients that support gum tissue repair and regeneration
• Deliver anti-inflammatory compounds that reduce gum inflammation
• Support the body's natural immune response in the mouth
Key Ingredients That Make a Difference
The most effective oral health supplements contain a carefully balanced combination of probiotics, vitamins, minerals, and botanical extracts. Here are the key ingredients that research has shown to be most beneficial:
Lactobacillus Reuteri
This probiotic strain has been extensively studied for its oral health benefits. Clinical trials have shown that L. reuteri can reduce gum bleeding by up to 60% and significantly decrease levels of harmful bacteria in the mouth. It works by producing natural antimicrobial compounds that selectively target pathogenic bacteria while promoting the growth of beneficial species.
Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in cellular energy production. In the context of oral health, CoQ10 helps repair damaged gum tissue and reduces inflammation. Studies have shown that people with gum disease often have lower levels of CoQ10 in their gum tissue, and supplementation can lead to significant improvements in gum health.
Vitamin C and Bioflavonoids
Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis, which is crucial for maintaining healthy gum tissue. Bioflavonoids enhance the absorption and effectiveness of vitamin C while providing additional anti-inflammatory benefits. Together, they support the repair and maintenance of gum tissue and help prevent bleeding gums.
Cranberry Extract
Cranberry extract contains proanthocyanidins, compounds that prevent harmful bacteria from adhering to teeth and gums. This anti-adhesion property helps reduce plaque formation and supports overall oral health. Studies have shown that cranberry extract can reduce the levels of harmful bacteria in saliva by up to 50%.
Natural Home Remedies That Actually Work
While professional dental care and targeted supplements form the foundation of optimal oral health, several natural home remedies have been scientifically proven to provide additional benefits. These time-tested approaches can complement your oral health routine and provide immediate relief for various oral health issues.

Oil Pulling: Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Oil pulling, an ancient Ayurvedic practice, involves swishing oil in your mouth for 10-20 minutes to remove bacteria and toxins. Modern research has validated this traditional practice, showing significant benefits for oral health.
A 2019 study published in the Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research found that oil pulling with coconut oil was as effective as chlorhexidine mouthwash in reducing harmful bacteria and improving gum health. The practice works by:
• Mechanically removing bacteria and plaque
• Reducing inflammation in the gums
• Improving overall oral hygiene
• Freshening breath naturally
🥥 Oil Pulling Protocol
Use 1 tablespoon of coconut oil (solid at room temperature, it will melt in your mouth). Swish gently for 10-20 minutes, then spit into a trash can (not the sink, as it can clog pipes). Rinse with warm water and brush your teeth normally. Practice oil pulling on an empty stomach for best results.
Green Tea: A Powerful Antioxidant for Oral Health
Green tea contains catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which have potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of green tea has been associated with improved gum health and reduced risk of oral cancer.

Research published in the Journal of Periodontology found that men who regularly consumed green tea had superior periodontal health compared to those who didn't. The study showed:
• Reduced gum bleeding and inflammation
• Lower levels of harmful bacteria
• Improved attachment of gums to teeth
• Reduced pocket depth in gum disease
Salt Water Rinses: Simple Yet Effective
Salt water rinses are one of the most accessible and effective home remedies for oral health issues. The antimicrobial properties of salt help reduce bacterial growth, while the osmotic effect helps reduce swelling and inflammation.
A proper salt water rinse can:
• Reduce bacterial load in the mouth
• Promote healing of minor cuts and sores
• Reduce gum inflammation and bleeding
• Provide temporary pain relief
To prepare an effective salt water rinse, dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of sea salt in 8 ounces of warm water. Rinse for 30 seconds, then spit out. Use 2-3 times daily, especially after meals.
Turmeric: Nature's Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with powerful anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Studies have shown that turmeric can be as effective as conventional treatments for gingivitis and other gum diseases.

A 2017 study in the Journal of Indian Society of Periodontology found that a turmeric gel was as effective as chlorhexidine gel in treating gingivitis. Participants who used turmeric gel showed:
• Significant reduction in gum inflammation
• Decreased bacterial counts
• Improved overall gum health scores
• No adverse side effects
Foods That Heal vs. Foods That Harm Your Oral Health
Your diet plays a crucial role in determining your oral health outcomes. While some foods actively promote healing and protect against disease, others can accelerate tooth decay and gum disease. Understanding which foods to embrace and which to avoid can dramatically improve your oral health.
Superfoods for Superior Oral Health

Leafy Greens: Nature's Tooth Protectors
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich in calcium, folic acid, and B vitamins that promote gum health. The high fiber content also helps stimulate saliva production, which naturally cleanses the mouth and neutralizes harmful acids.
Folic acid, in particular, has been shown to reduce gum inflammation and bleeding. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology found that people with higher folate levels had significantly better gum health and lower rates of periodontal disease.
Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Powerhouses
Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and other fatty fish are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have potent anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of omega-3s can help reduce gum inflammation and support the healing process.
Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people with higher omega-3 intake had a 30% lower risk of developing gum disease. The anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3s help modulate the immune response and reduce tissue damage.
Nuts and Seeds: Mineral-Rich Mouth Protectors
Almonds, walnuts, and seeds like sesame and pumpkin seeds provide essential minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium that are crucial for tooth enamel strength. They also contain healthy fats and protein that support overall oral health.
🥜 Snacking Tip
Choose raw, unsalted nuts and seeds for the best oral health benefits. The chewing action required to eat nuts also helps stimulate saliva production, providing additional cleansing benefits.
Probiotic Foods: Balancing Your Oral Microbiome
Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented foods contain beneficial bacteria that can help balance your oral microbiome. These foods introduce helpful bacteria that compete with harmful pathogens for space and resources in your mouth.
A 2018 study in the journal Nutrients found that regular consumption of probiotic foods was associated with improved gum health and reduced levels of harmful bacteria in the mouth. The beneficial bacteria in these foods can help:
• Reduce inflammation in the gums
• Compete with harmful bacteria for nutrients
• Produce antimicrobial compounds
• Support immune function in the mouth
Foods to Avoid: The Oral Health Destroyers

Sugary Snacks and Beverages
Sugar feeds the harmful bacteria in your mouth, leading to acid production that erodes tooth enamel and irritates gums. The frequency of sugar consumption is more important than the total amount – frequent snacking on sugary foods keeps your mouth in a constant state of acid attack.
Particularly harmful are:
• Sticky candies that cling to teeth
• Sugary drinks that bathe teeth in sugar
• Dried fruits with concentrated sugars
• Sports drinks and energy drinks
Acidic Foods and Beverages
Acidic foods and drinks can directly erode tooth enamel, making teeth more susceptible to decay and sensitivity. Common acidic culprits include:
• Citrus fruits and juices
• Tomatoes and tomato-based products
• Wine and other alcoholic beverages
• Carbonated beverages
While many acidic foods have nutritional benefits, it's important to consume them as part of meals rather than as standalone snacks, and to rinse with water afterward.
Processed and Refined Foods
Highly processed foods often contain hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives that can promote inflammation and disrupt the oral microbiome. These foods also tend to be low in the nutrients that support oral health.
When to Seek Professional Help: Red Flags That Require Immediate Attention
While many oral health issues can be managed with improved home care and nutritional support, certain symptoms require immediate professional attention. Recognizing these red flags can mean the difference between simple treatment and complex, expensive procedures.
🚨 Emergency Dental Situations
Seek immediate dental care if you experience: severe tooth pain that interferes with sleep or daily activities, facial swelling, fever accompanying dental pain, trauma to teeth or mouth, or sudden tooth loss. These situations can quickly become life-threatening if left untreated.
Progressive Symptoms That Shouldn't Be Ignored
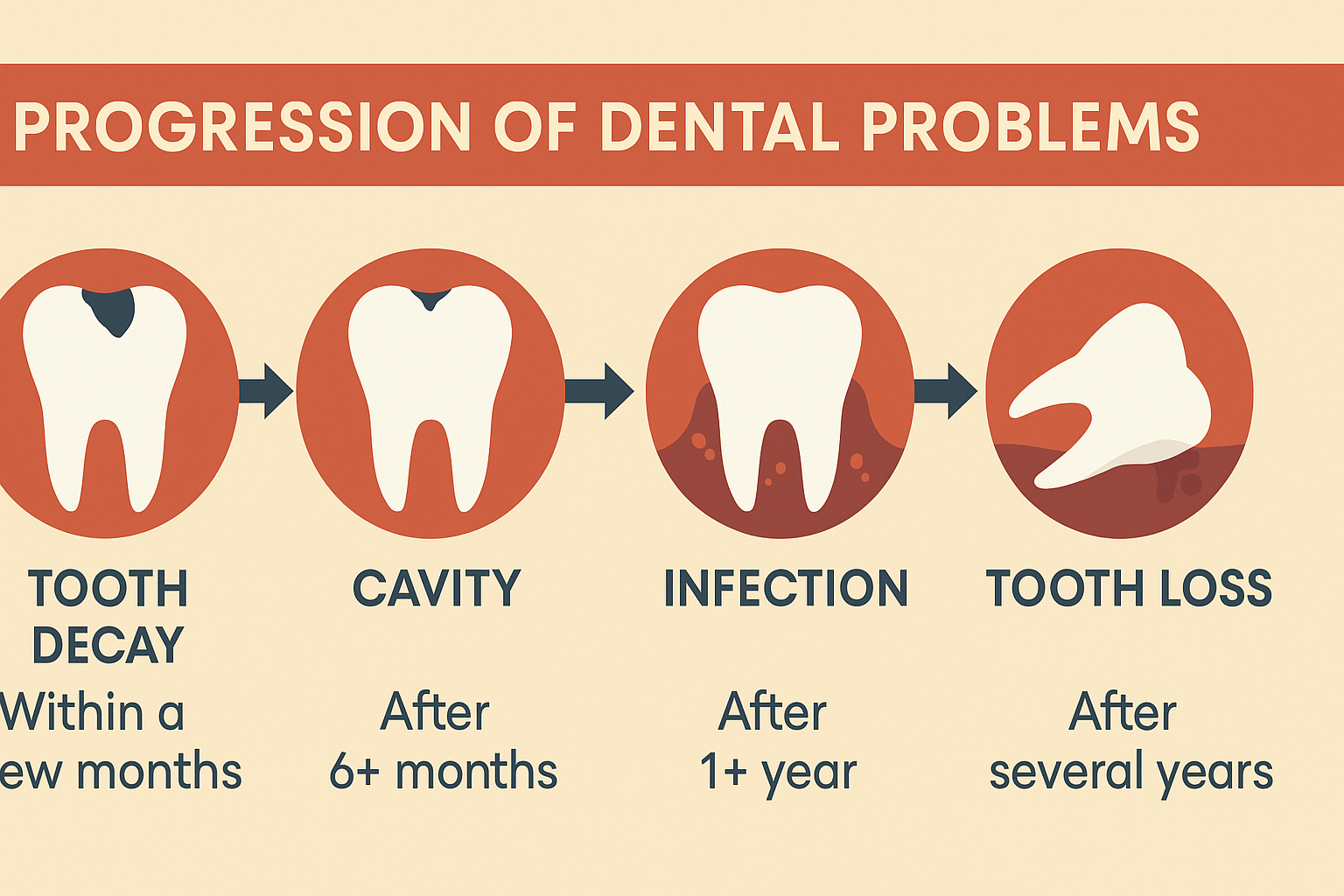
Many people delay seeking dental care due to cost concerns, dental anxiety, or the mistaken belief that problems will resolve on their own. However, dental problems rarely improve without intervention and often become more complex and expensive to treat over time.
Pain That Worsens or Persists
Dental pain is your body's warning system indicating that something is wrong. Pain that increases in intensity or duration, especially pain that wakes you at night, indicates serious infection or nerve damage that requires immediate treatment.
Swelling in the Face, Jaw, or Neck
Facial swelling associated with dental problems can indicate a serious infection that may spread to other parts of the body. This is particularly dangerous when the swelling affects the throat or breathing passages.
Pus or Discharge
Any pus or unusual discharge from the gums or around teeth indicates active infection that requires antibiotic treatment and professional intervention.
The Future of Oral Health: Emerging Technologies and Treatments
The field of oral health is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and treatments offering hope for better prevention and treatment of dental diseases. Understanding these emerging approaches can help you make informed decisions about your oral health care.
Precision Dentistry and Personalized Treatment
Just as medicine is moving toward personalized treatment based on individual genetic profiles, dentistry is beginning to embrace precision approaches that tailor treatment to each person's unique oral microbiome and genetic risk factors.
Advances in this field include:
• Genetic testing to identify susceptibility to gum disease
• Microbiome analysis to customize probiotic treatments
• AI-powered diagnostic tools for early disease detection
• Personalized supplement recommendations based on individual needs
Regenerative Dentistry
Researchers are developing ways to regenerate lost tooth and gum tissue using stem cells, growth factors, and tissue engineering techniques. These approaches offer hope for reversing damage that was previously considered permanent.
Nanotechnology in Oral Care
Nanotechnology is being applied to develop more effective toothpastes, mouthwashes, and dental materials. Nanoparticles can deliver active ingredients more precisely and provide longer-lasting protection against bacteria and acid erosion.
🌟 Take Action Today: Your Path to Optimal Oral Health
Don't wait until problems become serious. The best time to improve your oral health is now. Start with the most effective, science-backed supplements that can transform your oral health from the inside out.
Discover the Top 3 Supplements for Teeth & Gums →Based on extensive research and clinical studies, these supplements have helped thousands of people achieve better oral health naturally.
Creating Your Personal Oral Health Action Plan
Transforming your oral health requires a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of oral care. Here's how to create a personalized action plan that will deliver real results:
Phase 1: Assessment and Foundation (Weeks 1-2)
Begin by honestly assessing your current oral health status. Take note of any warning signs you've been ignoring and schedule a professional dental evaluation if you haven't had one recently.
During this phase:
• Document any symptoms or concerns
• Take photos of your gums and teeth for comparison later
• Begin implementing basic improvements to your oral hygiene routine
• Start incorporating oral health-supporting foods into your diet
Phase 2: Implementation and Optimization (Weeks 3-8)
This is where you implement the most impactful changes to your routine. Focus on consistency and gradual improvement rather than trying to change everything at once.
Key actions for this phase:
• Begin taking targeted oral health supplements
• Implement natural remedies like oil pulling or green tea rinses
• Optimize your diet by reducing harmful foods and increasing beneficial ones
• Establish consistent oral hygiene habits
Phase 3: Maintenance and Monitoring (Ongoing)
Long-term success requires ongoing commitment and periodic adjustments to your routine. Regular monitoring helps you catch problems early and maintain your progress.
Ongoing activities include:
• Regular professional cleanings and check-ups
• Continued supplementation and natural remedy use
• Periodic reassessment of your oral health status
• Adjustments to your routine based on results and changing needs
📊 Track Your Progress
Keep a simple oral health journal noting improvements in symptoms like bleeding gums, bad breath, or tooth sensitivity. This helps you stay motivated and identify what works best for your individual situation.
Conclusion: Your Journey to Optimal Oral Health Starts Now
Your oral health is far more important than you may have realized. The warning signs we've discussed in this guide are your body's way of alerting you to problems that could have serious consequences for your overall health and quality of life.
The good news is that most oral health problems are preventable and many are reversible with the right approach. By combining proper oral hygiene, targeted nutritional support, natural remedies, and professional care, you can achieve and maintain optimal oral health throughout your life.
Remember, the mouth is the gateway to your body's health. By taking care of your oral health, you're investing in your overall well-being and potentially preventing serious health complications down the road.
Don't wait until problems become serious. Start implementing the strategies outlined in this guide today, and consider adding scientifically-proven supplements to accelerate your progress and achieve the best possible results.
🎯 Ready to Transform Your Oral Health?
Take the first step toward optimal oral health with the most effective, research-backed supplements available. These carefully selected products have helped thousands of people achieve healthier teeth and gums naturally.
Get the Top 3 Supplements for Teeth & Gums →References and Scientific Sources
- American Dental Association. "Periodontal Disease". ADA.org, 2024.
- Genco, R.J., et al. "Periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease: epidemiology and possible mechanisms." Journal of the American Dental Association, vol. 133, 2002, pp. 14S-22S.
- Dominy, S.S., et al. "Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer's disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors." Science Advances, vol. 5, no. 1, 2019.
- Preshaw, P.M., et al. "Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship." Diabetologia, vol. 55, no. 1, 2012, pp. 21-31.
- Scannapieco, F.A. "Role of oral bacteria in respiratory infection." Journal of Periodontology, vol. 70, no. 7, 1999, pp. 793-802.
- Offenbacher, S., et al. "Maternal periodontitis and prematurity. Part I: Obstetric outcome of prematurity and growth restriction." Annals of Periodontology, vol. 6, no. 1, 2001, pp. 164-174.
- Shi, W., et al. "The oral microbiome: community composition, influencing factors, pathogenesis, and interventions." Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 11, 2020, p. 1476.
- Teughels, W., et al. "Clinical and microbiological effects of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotics in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized placebo-controlled study." Journal of Clinical Periodontology, vol. 40, no. 11, 2013, pp. 1025-1035.
- Nakayama, K., et al. "Coenzyme Q10 in gingival crevicular fluid and periodontal treatment." Journal of Clinical Periodontology, vol. 35, no. 3, 2008, pp. 233-240.
- Peedikayil, F.C., et al. "Effect of coconut oil in plaque related gingivitis — A preliminary report." Nigerian Medical Journal, vol. 55, no. 2, 2014, pp. 143-147.